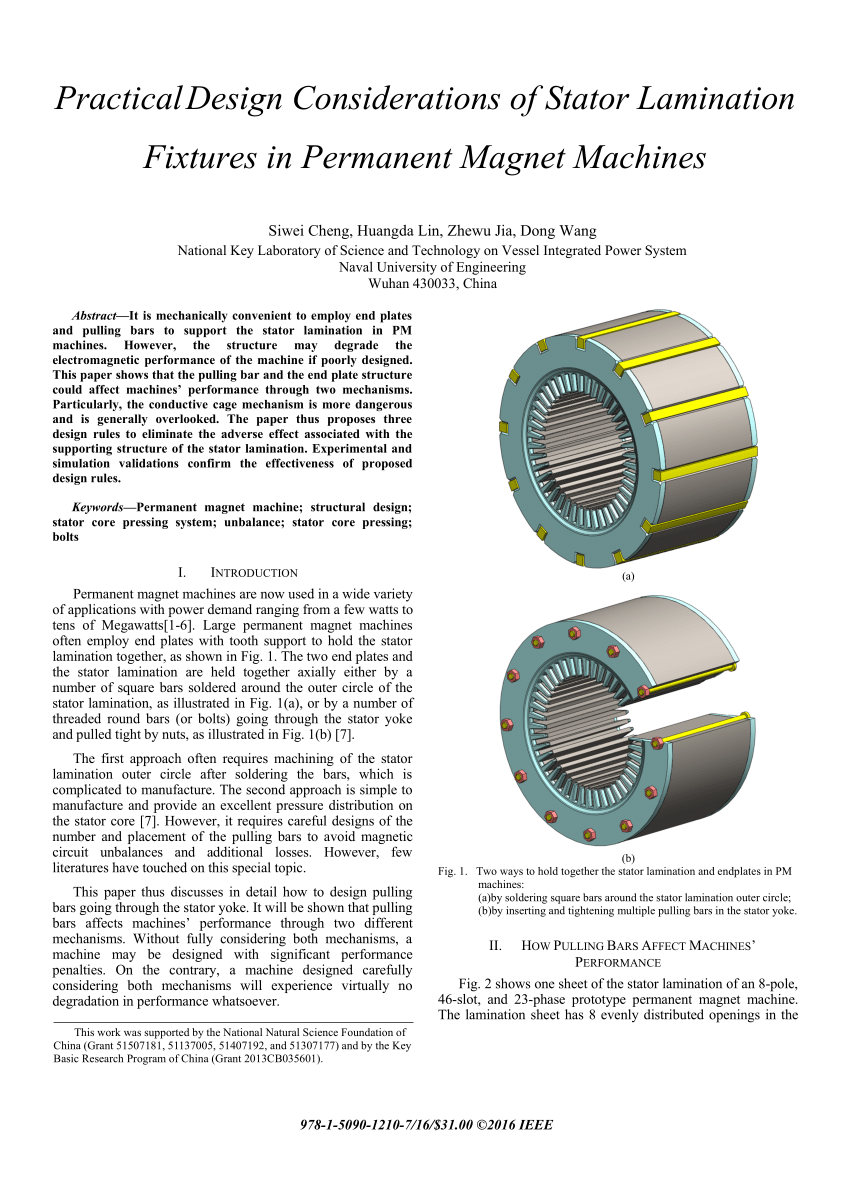
The laminations are basically round with a round hole inside through which the rotor is positioned.
Why is the stator core of synchronous machines laminated.
A stator core is built up as laminations are placed side by side in order to make a complete circular or ringed layer.
Thin silicon steel plates are stacked on top of one another around the center preventing eddy current flow.
The stator is not laminated in dc machines because it does not need to be laminated.
The stator core is made up of thousands tens of thousands or hundreds of thousands.
Heat often follows eddy current production.
Lamination is used in ac machines to prevent eddy currents from generating excess power due to the transformer.
Cools the stator core.
Stator laminations reduce eddy current by insulating the core.
This is described in faraday s law.
Where ever a coil is involved there will certainly be eddy current loss because of variation of magnetic field an e m f will be induced giving rise to current which does not contribute to the load rather gets wasted in the periphery of the coi.
This chapter discusses rotor and stator cores and in particular steel lamination and insulation on these laminations as well as how the laminations are fabricated into cores.
The stator core assembly of a synchronous machine is almost identical to that of an induction motor.
A major component of the stator core assembly is the core itself providing a high permeability path for magnetism.
If there s also a full circuit for the current to flow there.
Stator core laminations have a very specific profile and the dimensions have exacting tolerances.
The inner surface of the stator is made up of a number of.
The stator core is made up of a stack of round pre punched laminations pressed into a frame which may be made of aluminium or cast iron.
Currently laminations are manufactured by punching stamping dies or computer controlled laser cutting machines.
An alternating curren creates a constantly changing magnetic field.
A turbogenerator stator is comprised of two major components.
4 4 4 power angle of synchronous machines.
1 the stator windings and 2 the stator core.